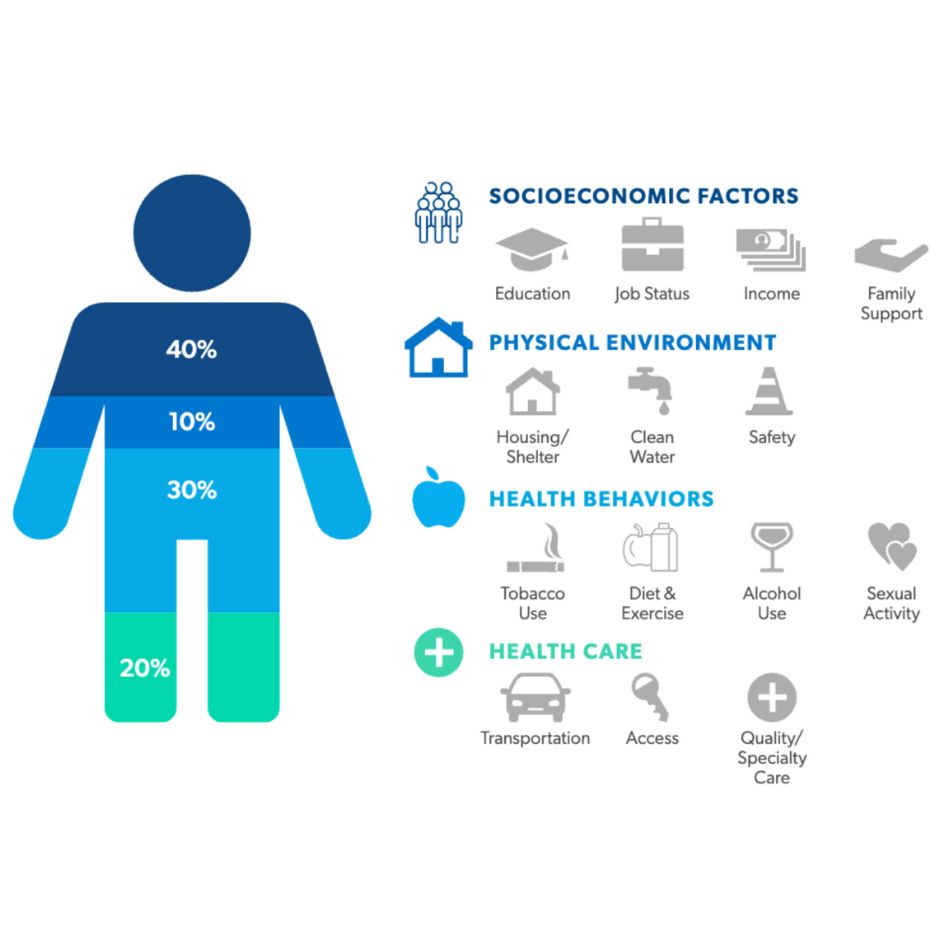
Amplify your existing systems with the Unified Care Exchange to connect Medicaid beneficiaries to the right services at the right time.
Talk to our team about a Unified Care Exchange program.
Do any of these frustrations sound familiar?
Blind Spots
Providers are often working with outdated and inadequate information and lack the historical context they need to fully support their patients.
Difficult Process
Already burdened patients must navigate this complex network, telling their story repeatedly to each provider they encounter.
Resource Challenges
Community-Based Organizations have a limited workforce facing multiple priorities, making it difficult to meet their clients’ needs.
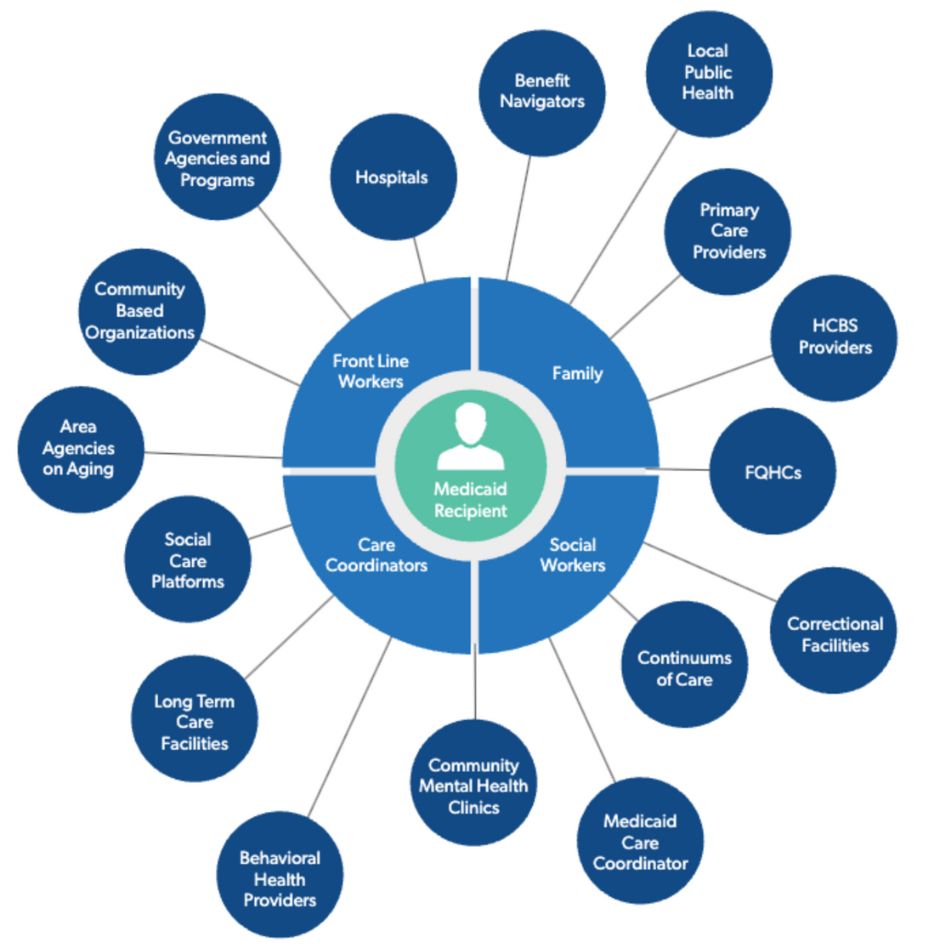
The Unified Care Exchange creates a person-centered focus, improving care coordination, service delivery, and decision-making.
Wherever you are in your Unified Care journey, we can help
Program Design and Planning
Readiness Assessment
Assess readiness across:
Lead Organization
System Implementation
FAQS
What does the Unified Care Exchange do to close the gaps in care?
The Unified Care Exchange (UCE) connects disparate systems to provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s clinical, behavioral, and social determinants of health (SDoH) data, ensuring all stakeholders have up-to-date information. By linking healthcare providers with housing, nutrition, transportation, and other community-based services, the UCE helps coordinate care across sectors to address unmet social needs that impact health outcomes.
How does the Unified Care Exchange provide an ROI?
By addressing social determinants of health (e.g., housing instability, food insecurity), a Unified Care Exchange can reduce costly acute care episodes. Improved coordination reduces duplication of services and waste, ensuring resources are directed where they are most needed. Providers and payers can avoid penalties for readmissions and poor outcomes under value-based care programs. The ROI is amplified when all stakeholders—healthcare providers, payers, and community organizations—collaborate effectively to achieve shared goals.
How does the Unified Care Exchange help if you’re understaffed?
By connecting healthcare and social services, the Unified Care Exchange reduces the need for staff to manually coordinate across multiple agencies. The UCE uses data to identify patients with the highest risks and most urgent needs, enabling staff to focus their limited resources where they can have the greatest impact. Built-in resource directories help staff quickly identify and connect patients to the right services, saving time spent searching for community resources.
What are the benefits to an individual if my agency implements the Unified Care Exchange?
For someone facing housing insecurity and chronic health issues, the Unified Care Exchange can connect them to housing assistance, mental health support, and primary care simultaneously, improving their stability and overall quality of life. Proactive care and early interventions lead to better health outcomes and greater stability in their social circumstances
How does the Unified Care Exchange lower costs in the Medicaid population while improving health outcomes?
Medicaid beneficiaries often use the ED for non-urgent issues due to unmet social needs or lack of access to primary care. By connecting patients to primary care, housing, food, transportation, and other resources, a Unified Care Exchange prevents avoidable ED visits, saving thousands per visit. Coordinating follow-up care and connecting patients to support services reduces complications post-discharge. By addressing SDoH through partnerships and referrals, the UCE tackles root causes, leading to healthier populations and lower healthcare costs. By connecting Medicaid beneficiaries to the right services at the right time, the UCE creates a more integrated care system that reduces costs while addressing the holistic needs of the population.
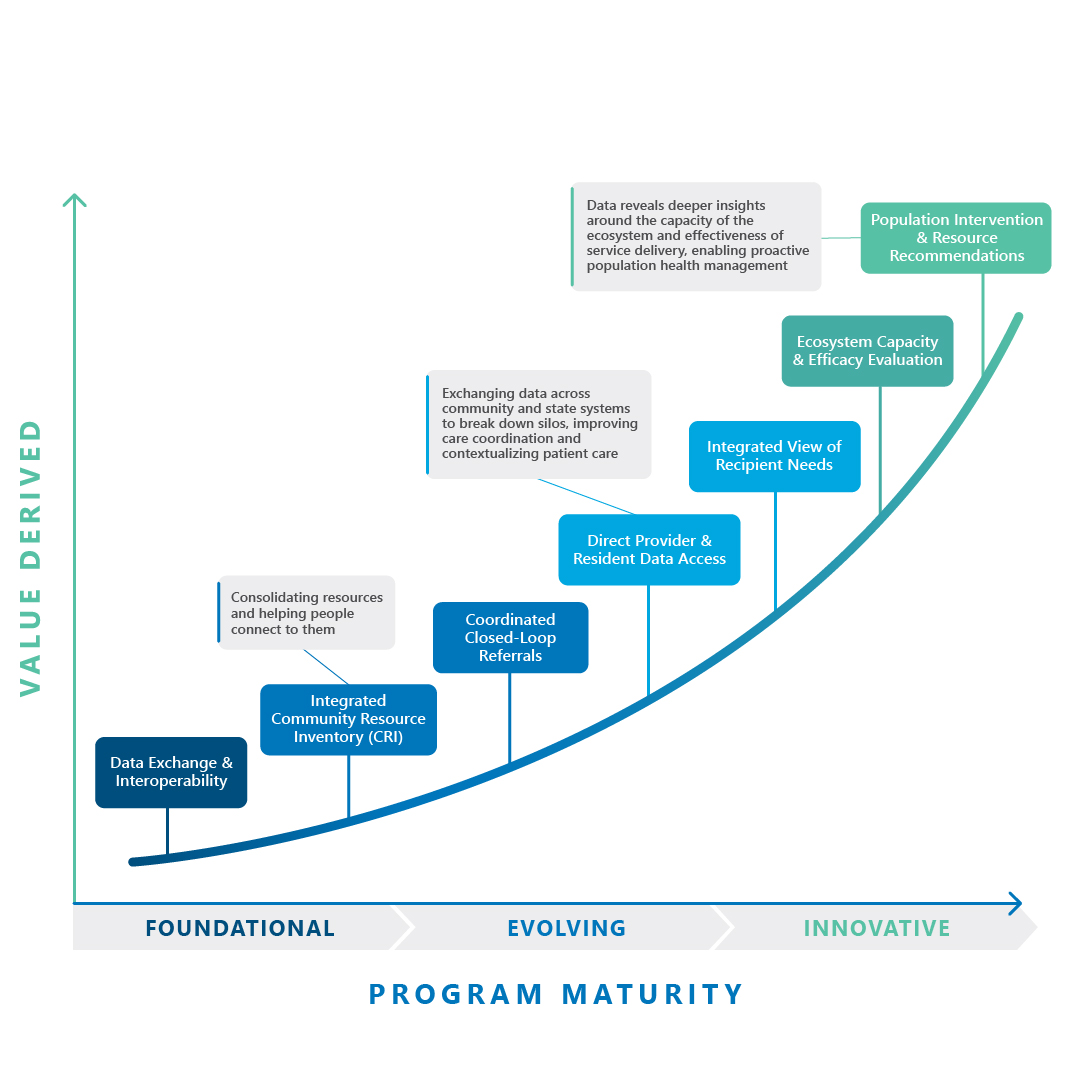
Unified Care Exchange can include new or enhance existing capabilities like:
Connect
Insights delivered to your inbox



